컴퓨터 네트워크 - 기본 개념
- Network Types (LAN, WAN)
- Network Criteria
- Physical topology
Computer network
- a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes
- The computers use common communication protocos over digital interconnections to communicate with each other
Internet
- the largest computer network
Networks
- the interconnection of a set of devices capable of communication
Connecting device
- ex) Router, Switch, Modem (moduator-demodulator)
Data
- information presented in whatever form is agreed upon by the groups creating and using it
Billions of connected computing devices
- hosts = end systems
- runninngs net work apps at Internets "edge"
-> 네트워크에 연결된 수많은 기기들 (핸드폰, 데탑, 태블릿 등...)
이들을 host = end system 이라함
end system 은 인터넷의 edge 에 위치해있기 때문에 Network Edge 라고도 함
Packet switches
- forward packets
- routers, switches
-> 패킷을 온전히 다 수신한 후 저장 (store-and-forward)
Network Types
LAN (Local Area Network)
- usually privately owned
- connects some hosts in a single office, building, or campus
- LANs today are connected to each other and to WANs to create communication at a wider level
WAN (Wide Area Network)
- also an interconnection of devices capable of communication
- has a wider geographical span
- interconnects connecting devices such as switches, routers, or modems
Network criteria (기준)
- Performance 성능
- Reliability 신뢰성
- Security 보안
Performance
- includes transmit time and response time
- transmit time : amount of time required for a message to travel from one device to another
- response time : elapsed time (경과 시간) between an inquiry and a response
Reliability
- the accuracy of delivery
- measured by the frequency of failure and the time it takes a link to recover from a failure
Security
- includes
- protecting data from unauthorized access
- protecting data from damage and development
- implementing policies and procedures for recovery from data losses
Physical topology
- the way in which a network is laid out physically
- topology of a network is the geometric representation of the links and nodes
- ex) Mesh topology, Star topology, Bus topology, Ring topology
Mesh topology
- every device has a dedicated point-to-point link to every other device
- need n(n-1) physical links
- every device on the network must have n-1 I/O ports to be connected to other n-1 stations

Star topology
- each device has a dedicated point-to-point link only to a central controller (switch or hub)
- does not allow direct traffic between devices

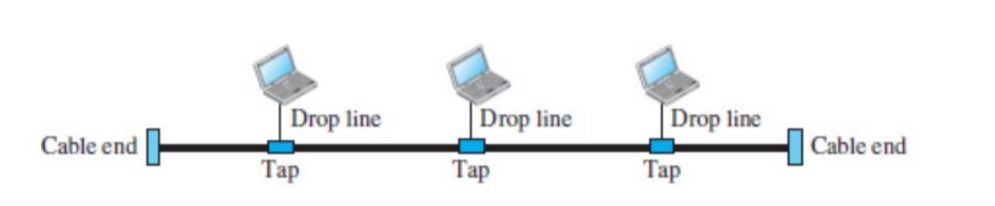
Bus topology
- multipoint
- one long cable acts as a backbone to link all the devices in a network
- drop line : a connection running between the device and the main cable
- tap : connector
Ring topology
- each device has a dedicated point-to-point connection with only the two devices on either side of it
- a repeater regenerates the bits and passes them along

'Computer Study' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [MySQL] 연산자와 부정 표현 (1) | 2023.10.09 |
|---|---|
| [SQL] SQL이란? + DDL, DML, DCL 개념 (1) | 2023.10.09 |
| [MySQL] MySQL 기본 기능 (0) | 2023.10.09 |
| [Computer Netwroks] TCP/IP Protocol Suite (0) | 2023.10.06 |
| [Computer Networks] Protocol Layering (프로토콜 계층화) (0) | 2023.10.06 |
